Geophysical
Survey Goals:
Locate previous excavations within the
archaeological grid
Identify potential burn pit features
Determine possible entry ways through the
the apparently continuous earthwork
structure
|
 |
  |
Site History:
Earthwork constructed between 1400 and 1650
AD
Located on bluff above old flood plain of
the Muskegon River
1937 excavations by Georgy Quimby
2006 excavations by Grand Valley State
University
2010 geophysical surveys
|
Stratigraphy
and Artifacts:
Sandy soils ideal for GPR surveys
Tree roots create moderate noise for GPR
Four Late Archaic Dustin/Lamoka points
One Early Woodland Kramer point
Numerous ceramics and lithics diagnostic of
Late Woodland/Late Prehistoric
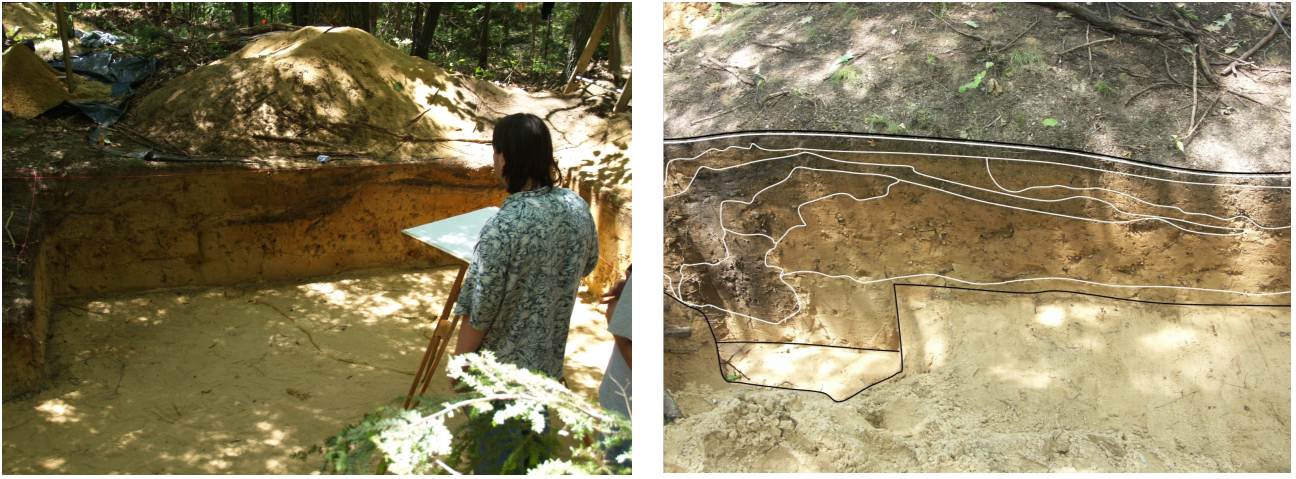
Two burn pit features (radiocarbon date
between 1400 and 1650 AD)
Worked native copper recovered from Feature
1 |
 |
|
Geophysical
Surveys:
Gentle
topography with leaf cover and numerous
small trees
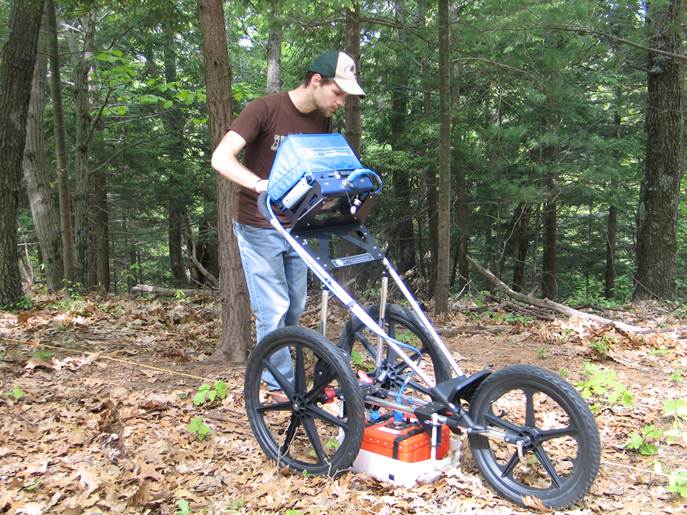
400MHz GSSI SIR 3000 GPR system
Geometrics G-858 Magnetometer/Gradiometer
42m x 44m grid
Bidirectional survey lines with a spacing of
1.0m
Magnetometer
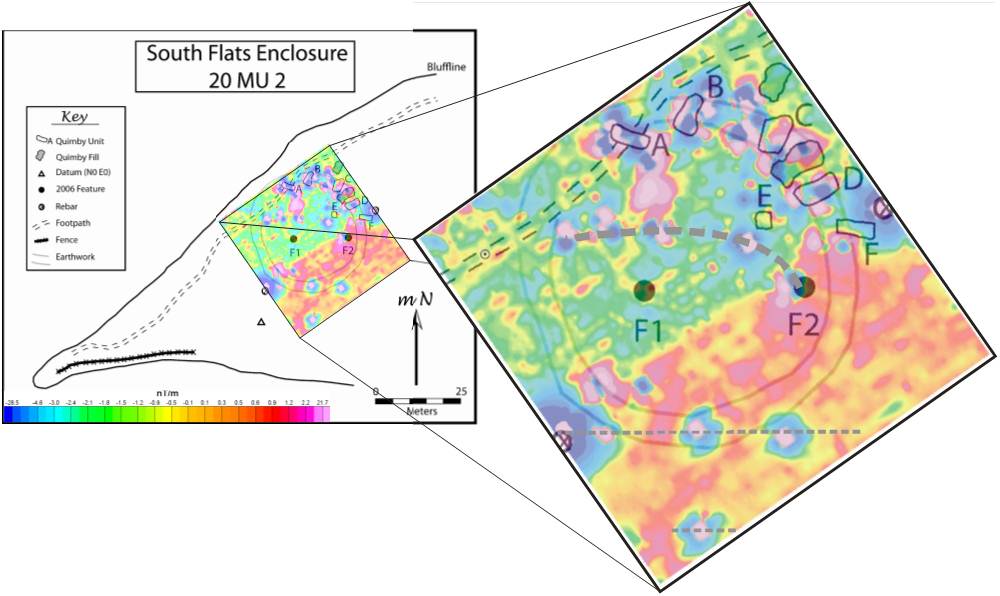
Data:
Background magnetic field
increases to the southeast
Feature 2 was not completely excavated in
2006 and is observed as a magnetic anomaly
An arc of magnetic anomalies similar to that
found at feature 2 is traced by the bold
dashed line which ends at feature 2 in the
east
Additional anomalous responses of unknown
origin are observed on the southern edge of
the survey area (two dashed lines) |
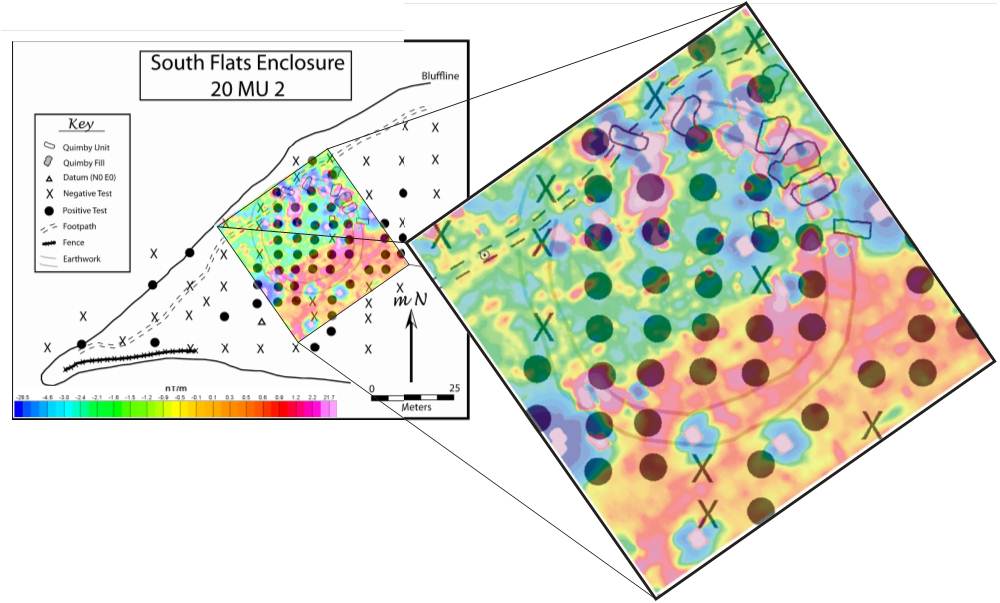
Pit Data:
1937 excavation pits
and 2006 reconstruction efforts create large
anomalies on the north edge
2006 excavations give indistinct geophysical
responses
Modern charcoal deposits south of A create
noise in the magnetic results
Positive shovel test pits indicate locations
of artifact removal prior to the 2010
geophysical surveys
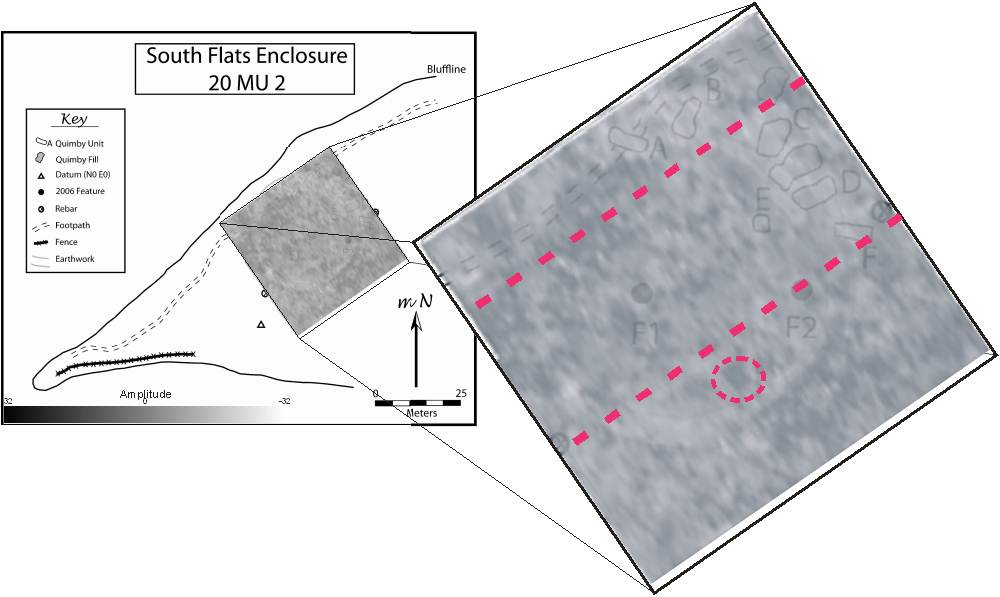
GPR Data:
Three dimensional GPR image illustrates the
circular earthwork structure at shallow
depth
Comparison of GPR and magnetic maps shows
correlation of anomalies at various depths
(example - dashed circle)
Two dimensional GPR profiles show many
hyperbolic reflections within the depth
range of artifact recovery (approximately
0.5m)
GPR results correlate to magnetic responses
with subsurface disturbance visible at the
locations of several magnetic anomalies
|
|
 |
Discussion:
Previous excavation units within the
archaeological grid were identified as
magnetic and GPR anomalies
Several potential burn pit features were
identified through both magnetic and GPR
methods.
The magnetic anomalies on the southern edge
of the survey area may relate to remnants of
an entry way |